Overview
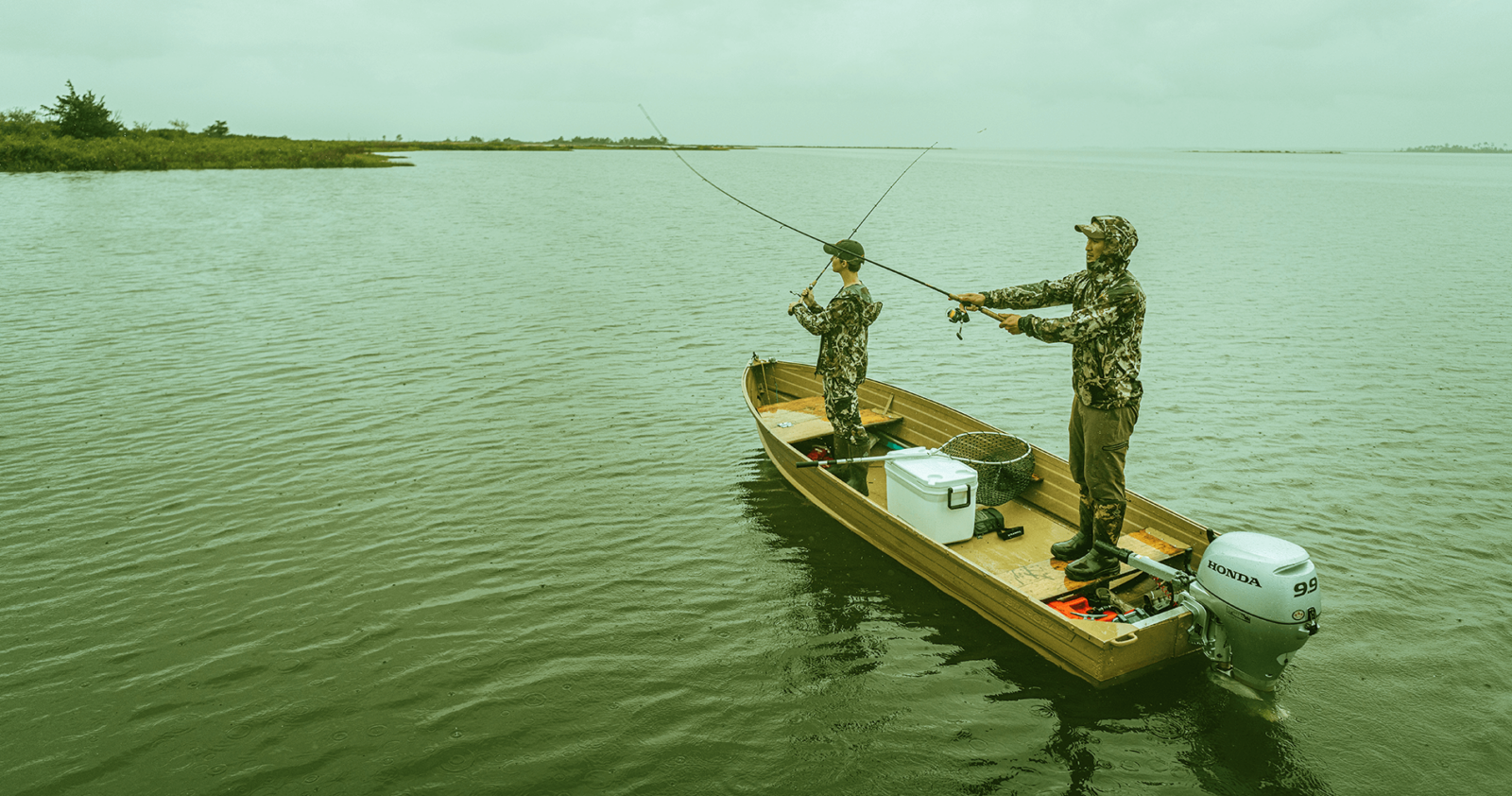
The Detroit River is not a river but classified as a strait in geography terms. The river is an important part of the Great Lakes system as it contains the busiest port. Use extreme caution when navigating the river due to heavy commercial and recreational boat traffic with fast currents and shallow waters in some areas. There are two dredged channels that lead from the mouth of Lake Erie to Lake St. Clair. One channel is used for upbound traffic and the other is used for downbound traffic. The navigation channels are clearly marked by a series of buoys and all navigation channels are dredged for the deep drafts on shipping boats.
Water levels can change up to 6- feet depending on the wind. If there is a strong east or west wind, Lake Erie will create pressure that can cause the water to in the mouth of the Detroit River to rise up to 6 feet higher. It has also been noted that during violent storms, the water level in western Lake Erie rises dramatically and causes water to flow upstream in the lower river. This is unique to the Detroit River.
To fish both sides of the river a Michigan and Ontario fishing license is required.
Frank and Poet Drain Map
Features
The Detroit River is an important part of the Great Lakes - and contains the busiest port on the Great Lakes. Approximately 10,000 commercial vessels use the Detroit River system yearly.Exercise extreme caution when navigating the river due to heavy commercial and recreational boat traffic and a fast current. The navigation channels are clearly marked by a series of buoys. All navigation channels are dredged to a minimum depth of 27 feet.The Detroit River is a major recreational boating area supporting approximately 75 commercial and private facilities. Michigan marinas are primarily located on Belle Isle, the mouth of the Ecorse River, the lower end of Grosse Ile and near Gibraltar.During violent storms, the water level in western Lake Erie rises dramatically and causes water to flow upstream in the lower river. This phenomenon is unique to the Detroit River.The upper river is normally ice-free, except for the shoal area between Belle Isle and the Michigan shoreline. In the lower river, ice develops in the shallow, protected island bays. The main navigation channels, however, generally remain open. Easterly winds can move Lake Erie ice into the lower river, causing ice jams which reduce current flow and hamper navigation.The yandotte National Wildlife Refuge, located along the lower river, is a gathering site for many migratory birds. Celeron, Grassy and Mud Islands provide important nesting habitat for resident and migratory birds. The lower end of the Detroit River is popular with duck hunters.There is presently no commercial fishery in the Detroit River, however, a significant bait fishery exists on the Ontario side. Approximately 7,200,000 baitfish per year are harvested and sold to bait dealers.The Detroit River supplies drinking water for approximately 3.9 million people. Detroit takes about 70 percent of its drinking water from the intake near Belle Isle.To fish both sides of the river a Michigan and Ontario fishing license is required.
Forage
Forage is diverse in the Detroit River with many native forage species such as emerald shiner, spottail shiner, sand shiner and gizzard shad. Small yellow perch and crayfish are favorite forage items for smallmouth. Muskie forage includes several spec
Seasonal Movements
The Detroit River is a migration route for many species of fish in the great lakes. Walleye, white bass, yellow perch and muskie move in and through the river system in spring, during their spawning runs. After their spawning run, majority the fish move between Lake Erie and Lake St. Clair. Both species of bass will run to the shallow marinas, river cuts and behind islands to spawn.

Get Your Line in the Right Water
Quickly find the best places to fish and plan your day right.
Top Fish Species
Understanding Abundance
Abundance ratings are based on Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE) measurements conducted by the MN DNR, and represent a snapshot of a species population at a given point in time
Source: Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Survey cadence may vary by state and water body.